Use Variables to store and retrieve information
Variables are used to store and retrieve user data in the conversations. They help to maintain context across different conversation steps.
You can use the variable to:
- Store data: Capture user inputs like names, locations, or preferences for later use.
Example: Save the user’s name as
getInput: user_name. - Retrieve data: Stored variables can be used to personalize responses, recall previous interactions, or pass information to external systems like APIs or databases.
- Maintain context: Variables help AI agents remember details throughout a conversation. This reduces the need for users to repeat information.
Types of Variables
- Session variables – Store temporary data throughout a conversation session. Data is lost when the session ends. Example: Remembering a user’s selected language preference during a chat session.
- Input variables – Capture user responses and store them as values for later reference.
Example: If a user enters their name, it can be stored as
getInput: nameand used in responses like: "Hello, getInput: name" - Output variables – Store processed data or results from backend integrations, API calls, or skills.
Example: Fetching order status from an API and storing it as
getInput: order_statusto display in the conversation. - System varibales: System variables are pre-defined variables available by default within the platform. These variables store details related to the user session, conversation context, and AI agent configuration.
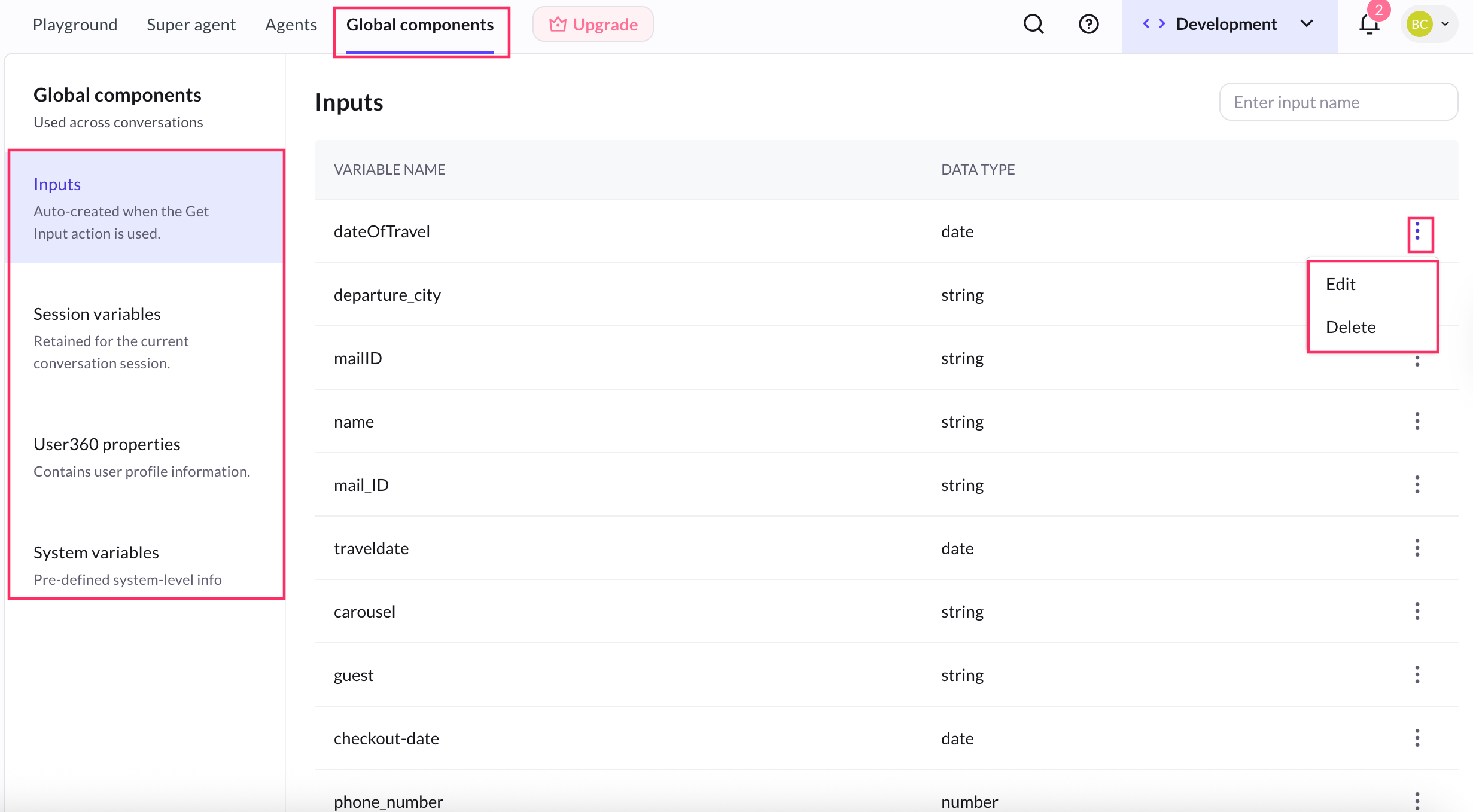
Manage Global variables
The Global Components section offers a unified view of all variables available to your AI agent.
It includes session variables, system variables, User 360, and output variables—all of which help manage conversation context and ensure consistent, personalized interactions. This includes:
- Session variables
- System variables
- User 360 variables
- Output variables
You can view, update, and test how data is use across the AI agent's conversations.
Key features:
- View variables: See all the variables that are currently being used across the conversation flows.
- Edit values: Modify the values of session or input variables for testing and preview purposes.
- Delete variables: Remove unwanted or outdated variables to keep your variable list clean and relevant.
- Search variables: Allows you to quickly search specific variables used in your AI agent’s conversation.
Pass variables in conversation
You need to pass the variables in between conversation for AI agents to remember user inputs throughout a conversation to avoid asking for the same information multiple times.
Example: If a user selects a flight in one step, the AI agent can remember it for later:
“You selected flight getInput: selected_flight. Do you want to proceed with booking?”
Use variables in responses
You can use variables in AI agent to make responses more dynamic and personalized.
Example:
Send a confirmation message to the user saying that your flight ticket is booked based on from {}var: departure_city to {}var: destination_city with a and {}var: booking_ID.
Pass variables in workflows
Variables are used to send and receive data between the conversation and the workflow to enable dynamic and context-aware interactions.
You need to pass the variables in the Workflow to access user inputs or previously stored values to perform logic, fetch data from APIs, or trigger actions. The results can then be passed back to the conversation using output variables.
How it works?
Input to Workflow:
When a Workflow is triggered during a conversation, you can pass variables (like user_email or order_id) into the Workflow.
These values are used inside the Workflow, for example, in an API request or Function.
Processing in Workflow:
The Workflow performs its tasks using the input variables (example, fetching user details using an email).
It may call APIs, run calculations, or retrieve records from a database.
Output from Workflow:
Once the Workflow completes, the Output node returns data as variables.
These output variables (example, account_balance or weather_description) can then be used in follow-up responses in the conversation.
Use case: A user wants to check their order status.
Conversation step:
AI agent asks: "Please enter your order ID". User replies: #12345
→ Input variable order_id is stored.
Workflow step:
The variable order_id is passed to the Workflow.
The Workflow calls an API using order_id to fetch order status.
The API response is mapped to an output variable like order_status.
Follow-up AI agent message:
Your order status is "order_status".
Best practices for using variables in workflows
- Always define input variables in the conversation and map them when triggering a Workflow.
- Use output variables from the Workflow to display dynamic information in later steps.
- Make sure variable names are unique and descriptive, and to avoid confusion (example, user_email, selected_flight, weather_info).
- If using APIs inside workflows, map response fields to output variables so they can be reused in the conversation.