AI agent overview
AI Agent builder is a no-code platform that simplifies the creation and deployment of intelligent AI agents. This platform simplifies the development process, by writing the prompts without extensive coding or technical expertise.
How it is different from traditional AI setups
Traditional NLP or Generative AI systems often require:
- Large training datasets
- Complex conversation flows
- Long and detailed prompts
With the AI Agent builder, it eliminates the need for complex setup:
- Simple setup: – Define your goal and select the tools or integrations you need.
- Faster setup – Build AI agents in minutes without writing scripts or creating complex flows.
- Dynamic handling – The agent dynamically manages responses and actions based on the use case.
AI Agents help businesses complete tasks, answer questions, and automate processes by using:
- Large Language Models (LLMs): These models provide the AI Agent with the ability to understand and respond in natural, human-like language.
- Workflows: Workflows define the step-by-step processes the agent follows to complete tasks.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Allow the AI Agent to connect with external systems and get real-time data or perform actions.
- Knowledge Base (KB): Knowledge Base serve as repositories of documents, FAQs, and data that the agent uses to give accurate answers.
Key benefits of AI agent:
- Faster development & go-live: Build and deploy AI agents in hours instead of months.
- Multi-modal, context-aware conversations: Engage users through chat, images, and rich media. The agent understands intent and smoothly manages context switches during conversations.
- Reduces operational costs: Eliminate the need for large development teams and reduce ongoing project and maintenance expenses.
- Greater flexibility and customization: Organizations can quickly experiment, adapt, and deploy new AI-driven solutions as needed.
AI Agent components
AI Agent builder follows a modular architecture designed to handle complex, multi-turn conversations across various business use cases. This architecture is built with three core components- Super Agent, Agents, and Knowledge Base agent, each playing a unique role in understanding user intent, managing conversation context, executing workflows, and delivering accurate, relevant information.
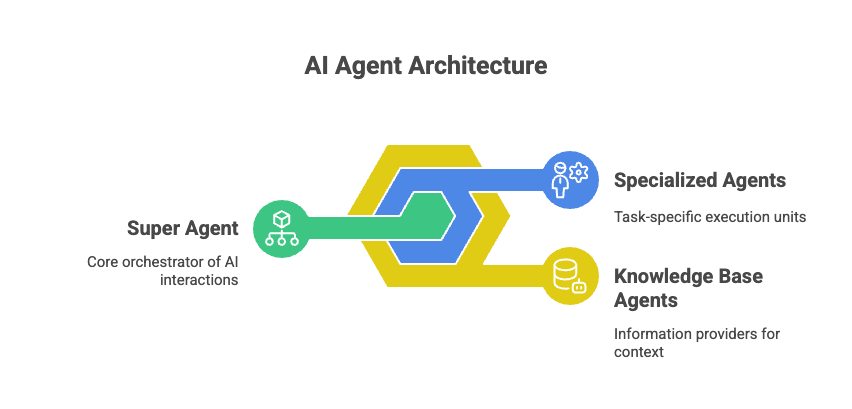
Super agent
The Super Agent functions as the central orchestrator of the entire AI agent system. Its primary responsibilities include understanding user intent, managing conversation context, handling initial greetings and fallback scenarios, and intelligently routing user queries to the most appropriate specialized agent.
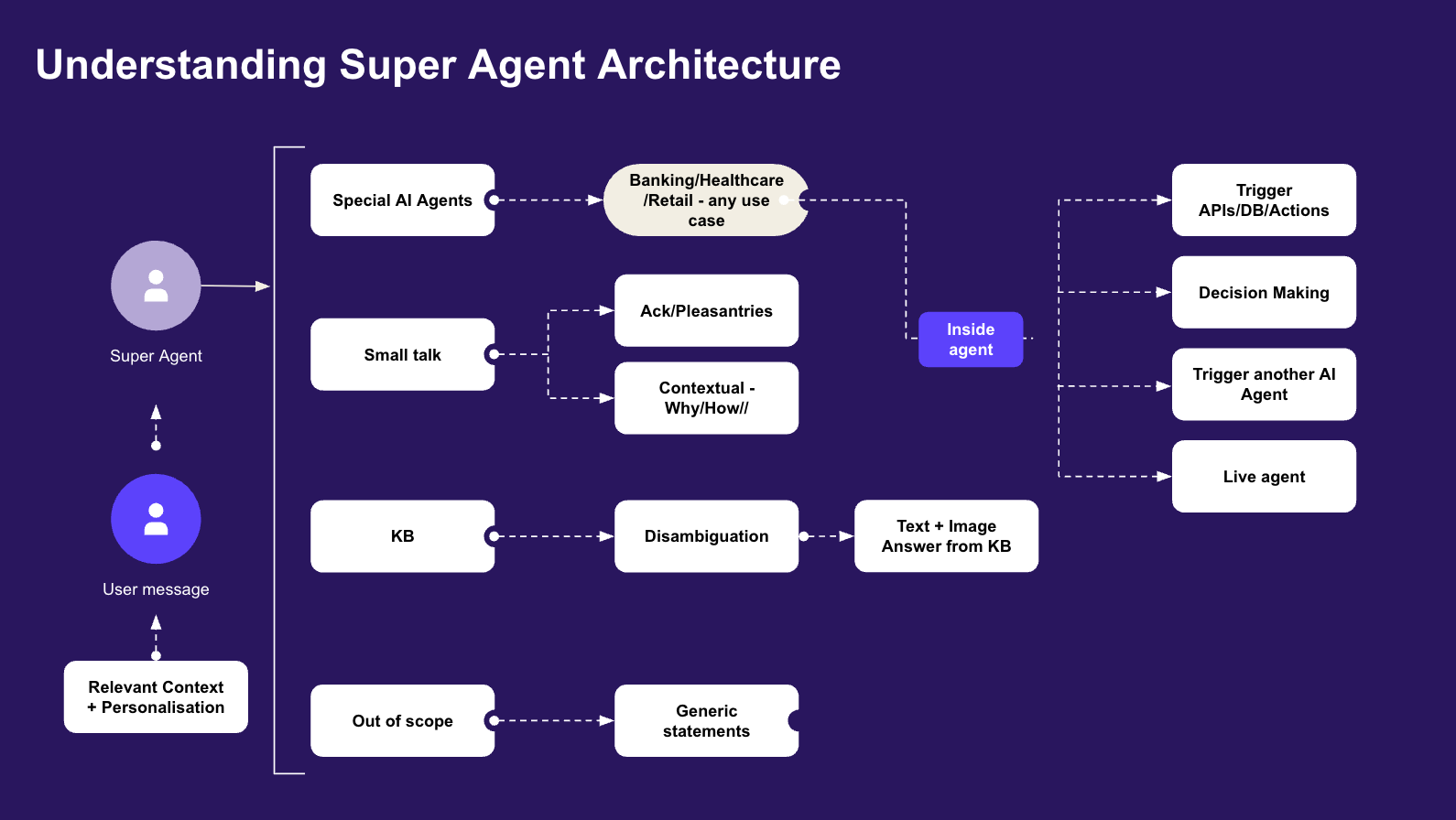
Key capabilities of Super agent:
- Understands user Intent using LLM: The Super Agent uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to analyze user input and accurately identify intent for effective conversation flow.
- Routes queries to the appropriate Agents: Directs queries to the right agent based on the detected intent to ensures that users are connected with the right expertise for their needs.
- Handles Welcome messages, Fallback, Small talk, and Custom rules: The Super Agent manages initial interactions with users, providing welcome messages and engaging in basic small talk to create a more natural and engaging experience. It also handles fallback scenarios when user input is unclear or cannot be processed, and uses custom rules defined for the overall agent behavior.
Agent
Agents are task-specific handlers designed to manage individual use cases within the AI agent system. Each agent is responsible for a particular domain, such as booking a flight, tracking an order, or raising a support ticket.
Key functions of Agent:
- Handle specific use cases: Agents are specialized to handle specific tasks or use cases. For example, a "Flight Booking Agent" would be responsible for managing all aspects of booking a flight, while an "Order Tracking Agent" would handle inquiries related to order status and delivery information.
- Collect input from the user using prompts: Agents interact with users by prompting them for the necessary information to complete the task. These prompts are designed to be clear, concise, and guide the user through the required steps.
- Trigger workflows to complete backend tasks: Once the agent has collected the necessary information from the user, it triggers workflows to execute backend tasks. These workflows may involve API calls to external services, database updates, system integrations, and other actions required to fulfill the user's request.
Knowledge Base agent
Knowledge Base Agents are designed to handle information-based queries by leveraging uploaded documents, policies, FAQs, and other connected data sources. They provide users with quick and accurate answers to their questions, drawing from a comprehensive knowledge base.
Key functions of Knowledge Base Agents:
- Responds to informational or FAQ-style queries: Knowledge Base Agents are specifically designed to answer questions that can be addressed by accessing and retrieving information from a knowledge base. This includes FAQs, policies, articles, and other informational resources.
- Searches and retrieves answers from uploaded Documents, Articles, Policies, and FAQs: The agent uses search algorithms and natural language processing techniques to efficiently search the knowledge base and retrieve relevant answers to user queries.
- Handles follow-up questions and provides summarized or contextual responses: Knowledge Base Agents can handle follow-up questions related to the initial query, providing additional details or clarification as needed. They can also provide summarized or contextual responses, tailoring the information to the specific needs of the user.
How AI agent component works together
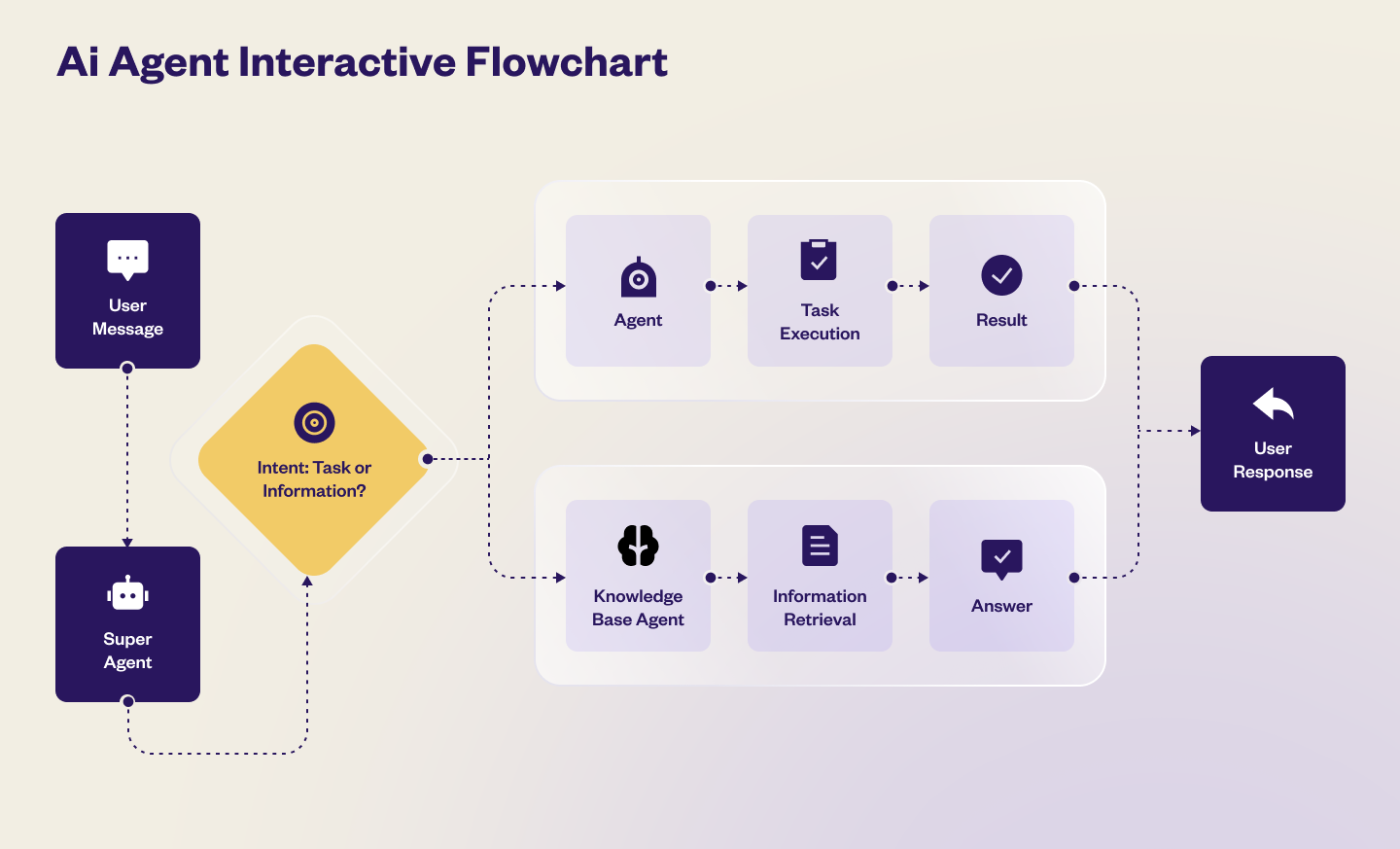
-
Super Agent – The Orchestrator The Super Agent is like a central controller. It gets the user's message first, figures out what the user wants, and decides where to send it: a. To a specific agent to handle intended/specialized task b. To the Knowledge Base (KB) Agent for information
- Or both a and b, if needed
-
Agent – The Task executor The Agent handles specific action where it can collect details, run workflows, call APIs, update records in database, or trigger events. Example: Booking a flight or cancelling a ticket.
-
Knowledge Base Agent – The information expert The KB Agent handles queries related to the product or services. It fetches information from the configured knowledge base and respond to users automatically based on the query. Example: Explaining refund policies or terms and conditions.
Configuration AI agent
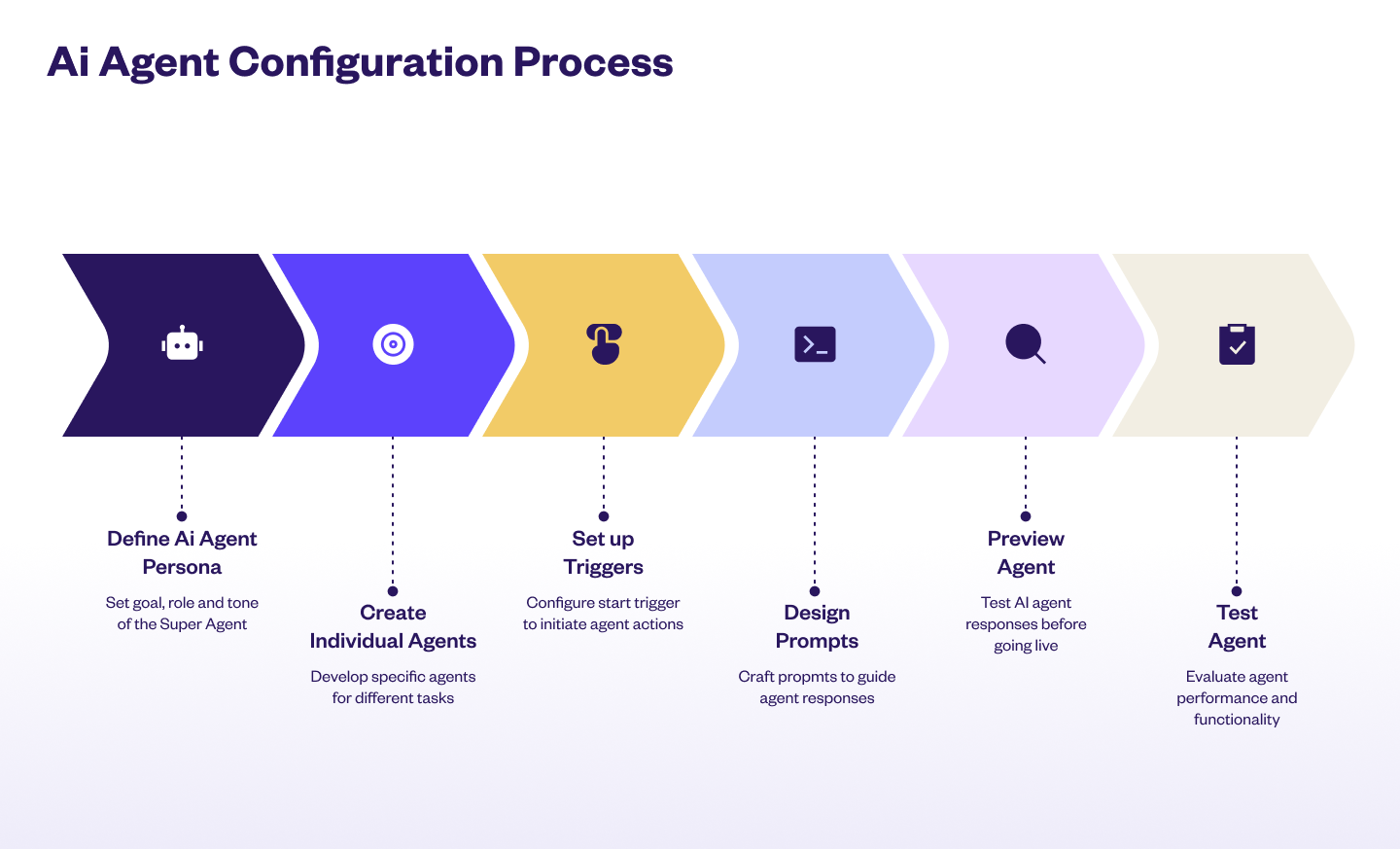
To set up your AI agent, follow these steps:
Step 1: Define the Super agent
- Define the role and scope of the Super Agent (for example, booking, cancellation, support).
- Choose the tone and style of communication (example, formal, friendly, witty).
ii. Integrate a Large Language Model (LLM)
- Integrate a Large Language Model (LLM) to empower the Super Agent with natural language understanding capabilities. The LLM enables the agent to interpret user queries, identify intents, and generate appropriate responses.
iii. Set Welcome and Fallback messages
- Create custom greetings to design personalized welcome messages to greet users upon initiating a conversation. These greetings should be engaging and informative.
- Create fallback responses to handle unclear or unrecognized user queries.
- Implement custom rules to enforce business logic. For example, require users to provide mandatory information, such as their email address or phone number, before proceeding with a transaction.
Step 2: Create individual agents
Set up dedicated agents for each use case. For example, create separate agents for booking a flight, canceling a ticket, or checking refund status. This allows each agent to focus on a specific area of expertise.
Step 3: Add Start trigger
The Start trigger initiates the conversation between the AI Agent and the user. Examples:
- A greeting like “Hi” or “Hello.”
- A specific keyword like “Book flight.”
Step 4: Add Prompts
Prompts are the messages your AI Agent sends to the user. You can make them static (simple messages) or dynamic (interactive messages with actions).
Add Actions in Prompts
While adding or editing a prompt, you can attach actions so the bot can collect inputs, trigger workflows, or store data.
i. Fetch user details: Use prompts to gather required information directly from the user, such as travel date, destination, or booking ID. This ensures the AI Agent has the necessary data to proceed with the next step.
ii. Trigger Workflow: Use this when you want the AI Agent to initiate backend processes after collecting inputs. For example, once the user provides a travel date and destination, the agent can trigger a workflow or API call to check flight availability.
iii. Variables: Store user inputs, such as travel dates, names, or booking IDs, as variables. These variables can be used to pass data between agents, workflows, and other components of the system.
Step 5: Preview agent
You can preview your AI Agent to test and experience how it interacts with users in real time. The preview simulates live conversations, allowing you to:
- Validate if prompts, workflows, and conversation rules are functioning as intended.
- Observe how the conversation flows from one step to another.
- Identify and fix issues before publishing the agent.
Step 6: Test your agent with Copilot
Before deployment, validate your AI Agent to ensure it behaves as intended and provides a consistent user experience. Copilot allows you to simulate real user interactions, helping you:
- Test diverse scenarios and input variations.
- Identify issues, errors, or gaps in the conversation flow.