Automation overview
Automation is the central workspace to build, orchestrate, and optimize Agentic AI. It brings together key capabilities such as AI Agent creation, workflow automation, database and API integration, and end-to-end testing
You can use the Automation module when you want to:
- Build AI agents that automate user conversations and tasks.
- Design workflows, connect backend systems via APIs, or store and retrieve data using a built-in database.
- Test and validate the agent's behavior and performance before going live, using Copilot sessions or by running test suites.
Watch the introductory video on Automation:
Automation module capabilities
The Automation module allows you to design and manage AI agents by combining AI-driven agents, rule-based agents, workflows, integrations, and testing tools to deliver seamless user experiences.
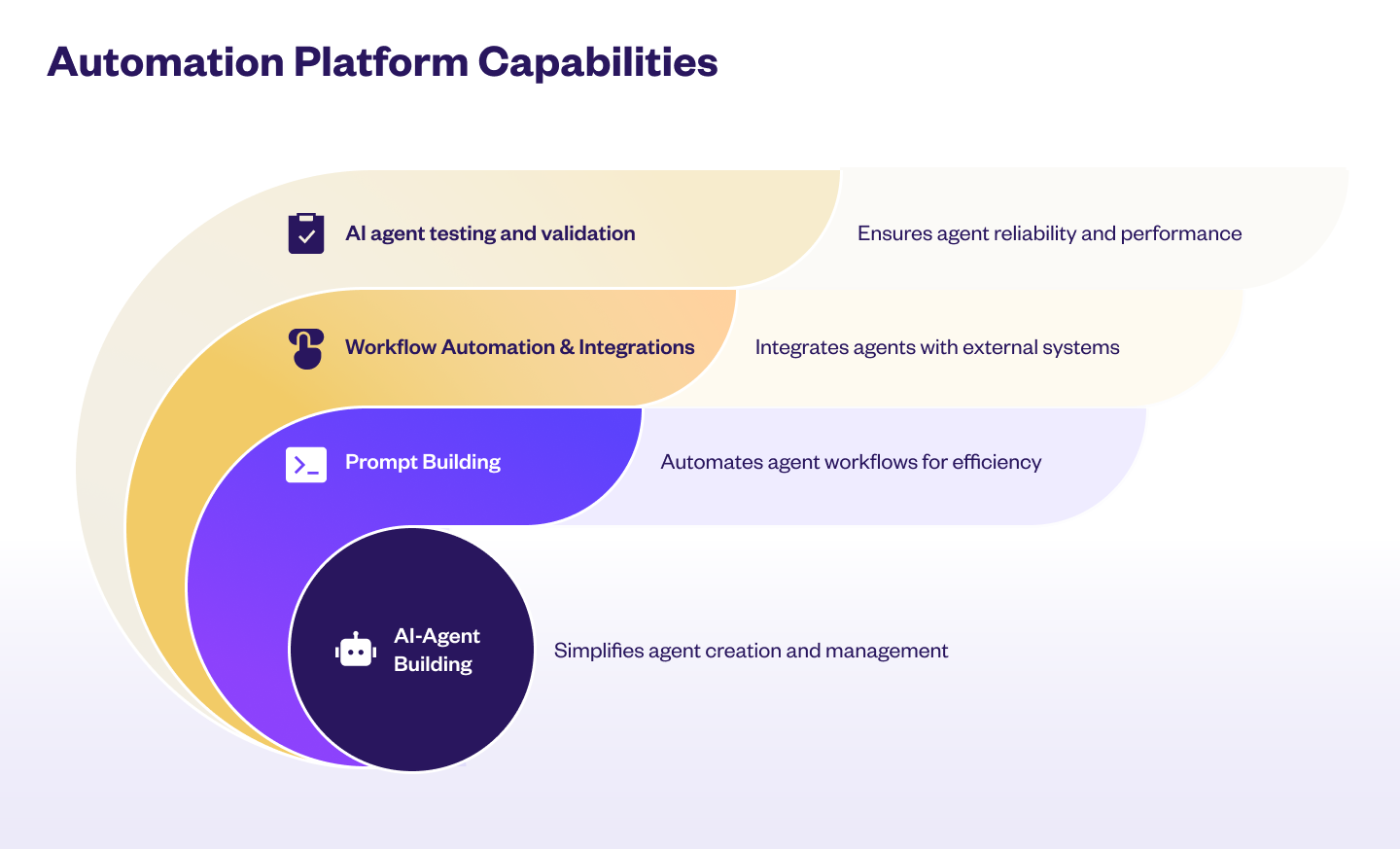
Key capabilities of the Automation module include:
- AI-Agent building: This is the core capability of the platform, which allows you to design and configure AI agents.
- Provides no-code interface to build agents.
- Supports both AI-driven and rule-based agents.
- Allows defining start trigger, prompts, workflows, conversation flows, and integrating business logic.
- Simplifies deployment and scaling of agents across different channels (web, mobile, chat apps).
- Workflow automation and integrations: Handles backend tasks that support the conversation. When triggered, it can call APIs, update database, or perform other automated actions to complete user requests.
- Both AI-driven and rule-based agents rely on workflows to complete user requests.
- Automates backend processes like API integrations, data processing, or business logic. Example: Order tracking, appointment booking, ticket management, and so on.
- Integrates with external systems such as CRMs and third-party applications to enable end-to-end automation.
- Automated AI testing: Testing ensures that your AI Agent works as expected before going live. The platform provides two testing approaches:
- Copilot: Allows you to manually test the AI Agent in a development environment.
- Manual testing tool that simulates real user conversations in a development environment.
- Allows validation of prompts, workflows, Knowledge Base responses, and conversation logic.
- It helps to validate tone, accuracy, and flow before publishing.
- Useful for quick debugging during the agent development.
- Test suites: Allows you to automatically test your AI agent’s functionality, performance, and accuracy without the need for manual testing.
- You can generate test cases to validate agent behavior.
- Provides detailed reports highlighting passed and failed cases.
- Ideal for regression testing and validation.
- Copilot: Allows you to manually test the AI Agent in a development environment.
Overview of Agentic architecture
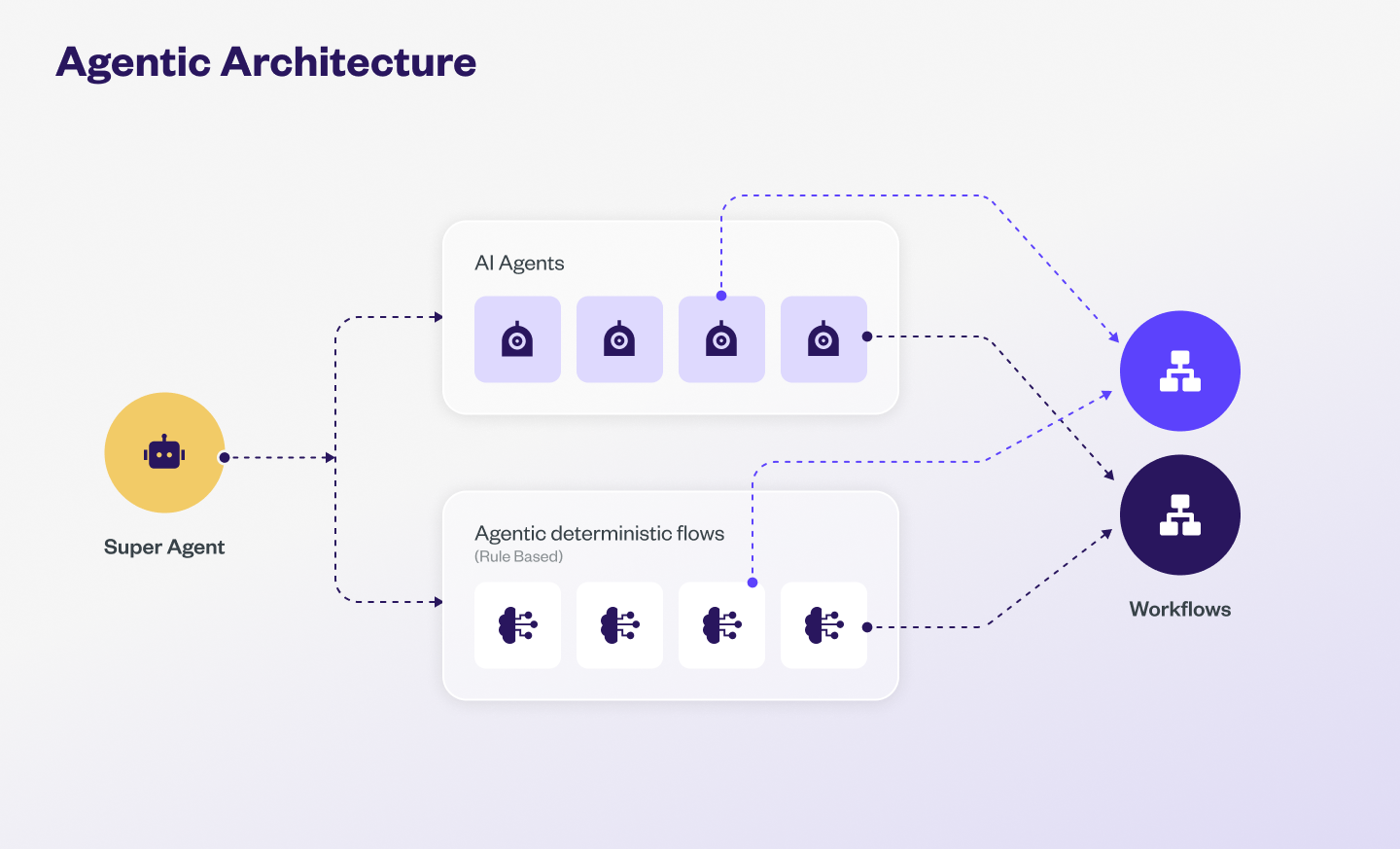
The Agentic architecture in Yellow.ai’s Automation module orchestrates conversations by combining AI-driven intelligence, rule-based logic, and workflows.
- AI-driven agents – Powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), these agents understand context, handle complex or multi-turn conversations, and generate natural, human-like responses. Ideal for open-ended queries and tasks that require reasoning or dynamic information retrieval.
- Rule-based agents(Deterministic agents) – These agents operate using structured logic and predefined nodes, progressing through deterministic workflows. Best suited for repetitive tasks such as booking forms, order tracking, or surveys.
- Workflows – Workflows act as the backend processes that agents invoke to perform actions like API calls, database updates, sending notifications, or triggering automated tasks. Both AI-driven and rule-based agents depend on workflows to complete tasks and maintain seamless conversation flow.
Camprision between AI-driven agents and Rule-based agents
| Aspect | AI-driven agent | Rule-based Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to interpret context and make dynamic decisions. | Uses structured logic and predefined rules to guide conversations. |
| Conversation handling | Handles complex, multi-turn, and open-ended conversations. | Handles linear, step-by-step conversations suited for predictable scenarios. |
| Context awareness | Retains and uses context from previous interactions to provide personalized responses. | Relies on predefined conditions and user inputs to guide conversations. |
| Flexibility | Adapts to varied user inputs and handle unexpected queries. | Follows rigid flows and handle only predefined scenarios. |
| Use case | Best for customer support with complex queries, troubleshooting, dynamic FAQs, and personalized recommendations. | Best for booking processes, order tracking, surveys, feedback collection, and other structured requests. |
AI agent components
Super agent
Super agent acts as the central orchestrator of all conversations within the AI agent. It intelligently routes user queries to the appropriate agent whether an AI-driven agent for complex, context-rich conversations or a rule-based agent for structured, deterministic workflows based on the query, conversation context, and predefined criteria.
Agent
Individual agents help to focus on specific conversation tasks, such as booking tickets, handling cancellations, or answering product-related queries.
The Super Agent coordinates these interactions by analyzing the user’s intent and routing the query to the most relevant agent. For example, if a user asks about refund eligibility, the Super Agent will trigger the Refund Agent, while a booking query would be directed to the Booking Agent.
Knowledge Base (KB) Agent
The Knowledge Base agent is a specialized AI-driven component designed to handle knowledge-intensive queries. It retrieves, summarizes, and delivers answers from knowledge sources like documents, FAQs, or external systems. It also supports follow-up questions, multilingual responses, and context-aware answers.
Rule-based agents
Rule-based agents, also known as node-based flows, are a key component of the agentic architecture. Unlike AI agents that rely on LLMs for contextual reasoning, rule-based agents operate through predefined paths and mapped intents. They are best suited for scenarios where interactions must follow a structured, predictable sequence such as authentication, form-filling, or survey collection.
In this setup, the Super agent determines when a conversation should follow a rule-based flow and routes the user to the appropriate agent. The rule-based agent then executes the step-by-step conversation paths to guide the users.
Nodes in rule-based Agents
In rule-based agents, nodes act as the fundamental building blocks of the conversation. Each node represents a specific action such as asking a question, validating input, branching logic, or triggering backend processes. By linking nodes together, these agents create structured paths that guide users to the desired outcome.
Nodes are useful for:
- Collecting information: Capture user inputs like name, email, phone number, preferences, or booking details. Example: Asking the user for their flight date or delivery address.
- Conditional branching: Direct the conversation along different paths based on user inputs. Example: If a user selects "Yes" → proceed to payment, if "No" → proceed to next step.
- Fetching data: Retrieve information from databases, APIs, or external systems. Example: Fetching flight availability, order status, or user account details.
- Data pushing / Backend integration: Send collected information to external systems or databases for processing. Example: Storing booking details in a Database.
- Mathematical and Logical Operations: Perform calculations or validations during the conversation using Functions. Example: Calculating total cost, validating an age or date, or checking inventory.
- Dynamic rich media generation: Create interactive and engaging responses using carousels, images, and quick replies. Example: Displaying flight options in a carousel or showing payment instructions with buttons.
- Triggering Workflows or APIs: Initiate automated workflows or external API calls from within the conversation.
Workflows in AI-powered Agents and Rule-based Flows
Workflows are specialized automation that agents call during a conversation to perform backend tasks, such as making API calls, updating database, or sending notifications. Both AI-powered agents and rule-based flows can use workflows, but they trigger them differently:
- AI-powered agents – Use the Call Workflow action within the prompts to trigger a workflow. This allows the agent to dynamically process user input, fetch data, or complete actions before continuing the conversation.
- Rule-based agents – Use the Execute node to call a workflow from a predefined step in the conversational flow.