Copilot debugger
Copilot debugger is a specialized AI agent designed to help developers and AI agent designers quickly identify and resolve issues across various components of their conversational agents. It helps to analyze common problems such as misconfigured prompts, incomplete workflows, missing API integrations, gaps in Knowledge base responses.
The goal of the Copilot bebugger is to improve AI agent performance by:
- Detecting failures or misconfigurations in the AI agent's responses
- Minimizing hallucinations and inaccurate replies
- Ensure AI agent logic (especially prompts) aligns with user inputs
- Saving time by offering ready-to-use resolution strategies
How it works:
The Copilot bebugger analyzes your AI agent’s configuration based on the problem description by the user. It examines key components such as prompts, workflows, APIs, and Knowledge base settings and compares them against the expected behavior to identify mismatches or misconfigurations.
When an issue is detected, the debugger:
- Pinpoints the exact path of the issue (example, a specific prompt or workflow node)
- Displays the current configuration, helping you understand what’s misaligned
- Recommends an updated version of the configuration to resolve the issue
You can also provide an optional expected output, which helps the debugger refine its analysis and recommendations for better accuracy.
The debugger is capable of detecting issues in the following components of the AI agent setup:
- Prompts: Verifies whether the configured prompts are clear, complete, and aligned with the expected bot behavior.
- Workflows: Checks if the workflow nodes are correctly set up and whether they support the required logic (example, missing API calls).
- Agents: Identifies problems in agent-level conversations, including missing triggers or configuration gaps.
- Super agent: Reviews overall setup such as welcome messages, tone, persona, and agent routing logic.
- APIs: Validates API connections and checks for missing or incorrect API configurations within workflows.
- Knowledge base (Kb): Ensures the KB Agent is correctly set up to handle knowledge-based queries, and flags if any relevant document or intent is missing.
How to use Copilot debugger
To use the Copilot debugger, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Automation > Copilot.
-
In the input chat field, enter the intent or message that you would like the AI agent to handle. This helps simulate the conversation flow where the issue occurs.
-
Click the Debugger icon next to the message field to initiate the debugging process.
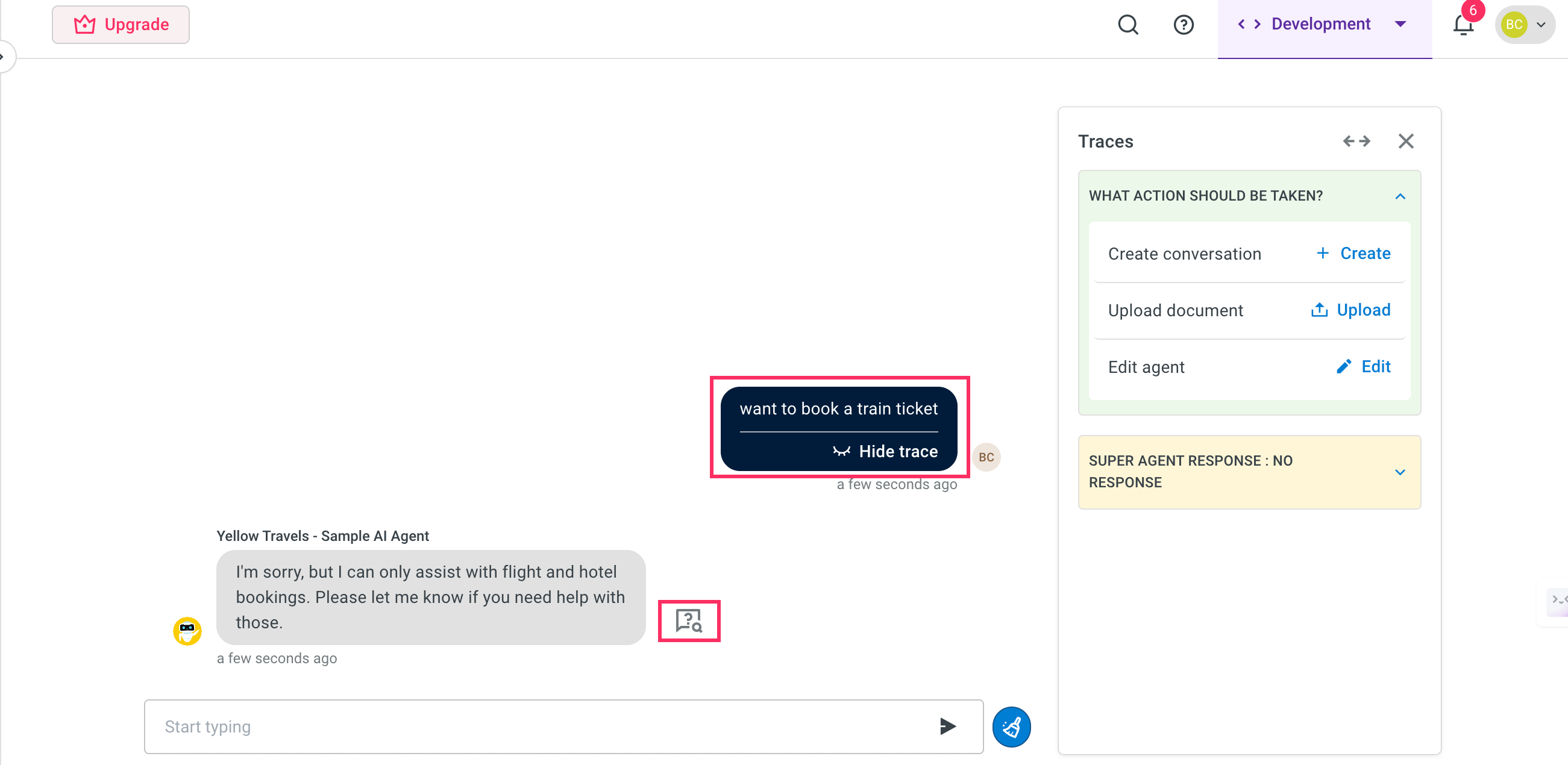
- The debugger will now guide you through identifying issues and suggest possible fixes.
Inputs processed by the debugger
To begin debugging, the Copilot debugger requires specific inputs that help it analyze the issue accurately and provide relevant suggestions.
-
Provide the following inputs:
i. Describe problem (required): Provide a clear explanation of the issue you are facing. Example: "The AI agent does not confirm the flight booking after user selects a flight".
ii. Expected answer (optional): If you expect the AI agent to respond in a particular way, you can specify the expected output here. This helps the debugger compare the actual behavior with your intended outcome. Example: "Your flight from Delhi to Mumbai has been successfully booked."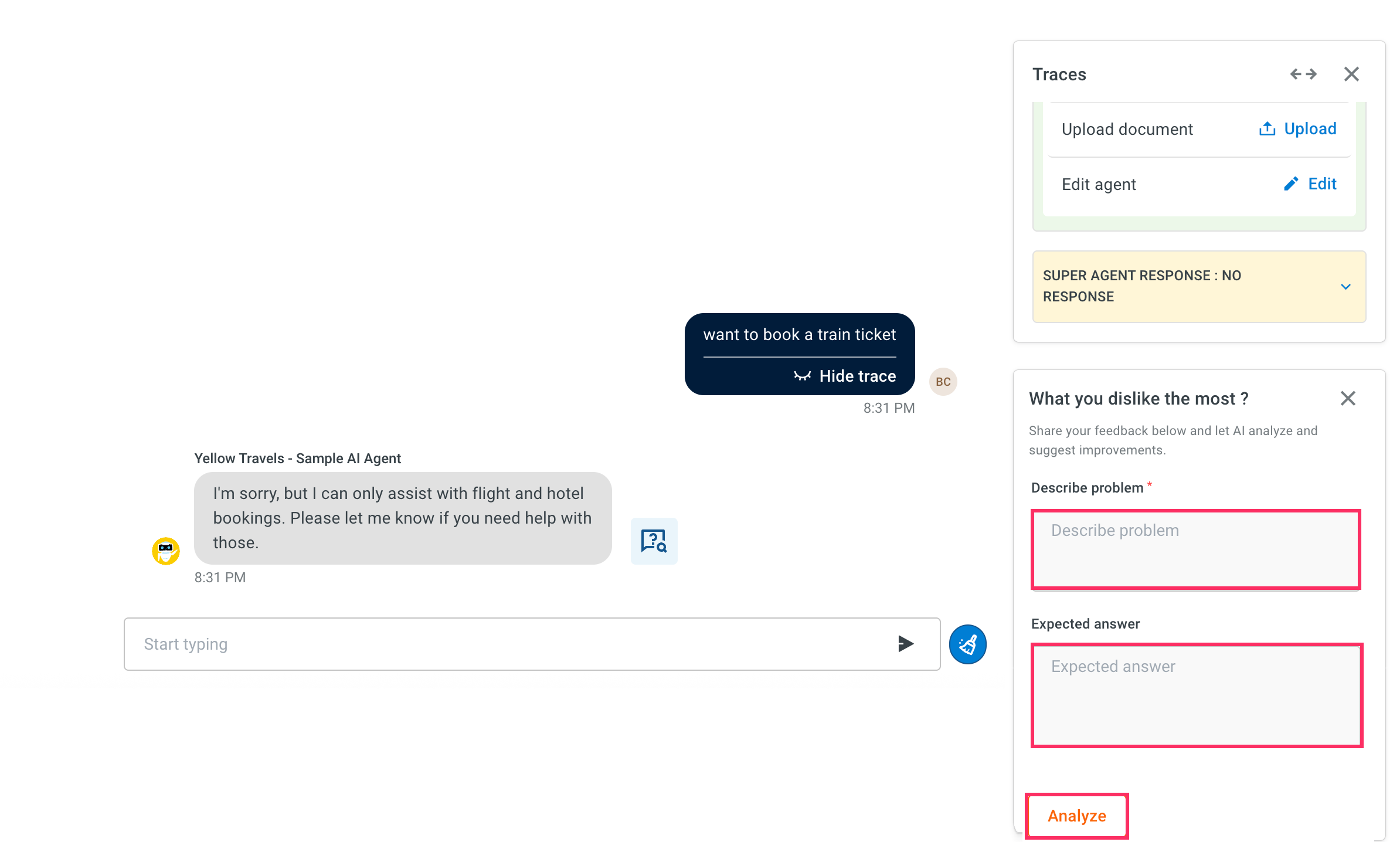
-
Click on Analyze to begin the debugging process.
-
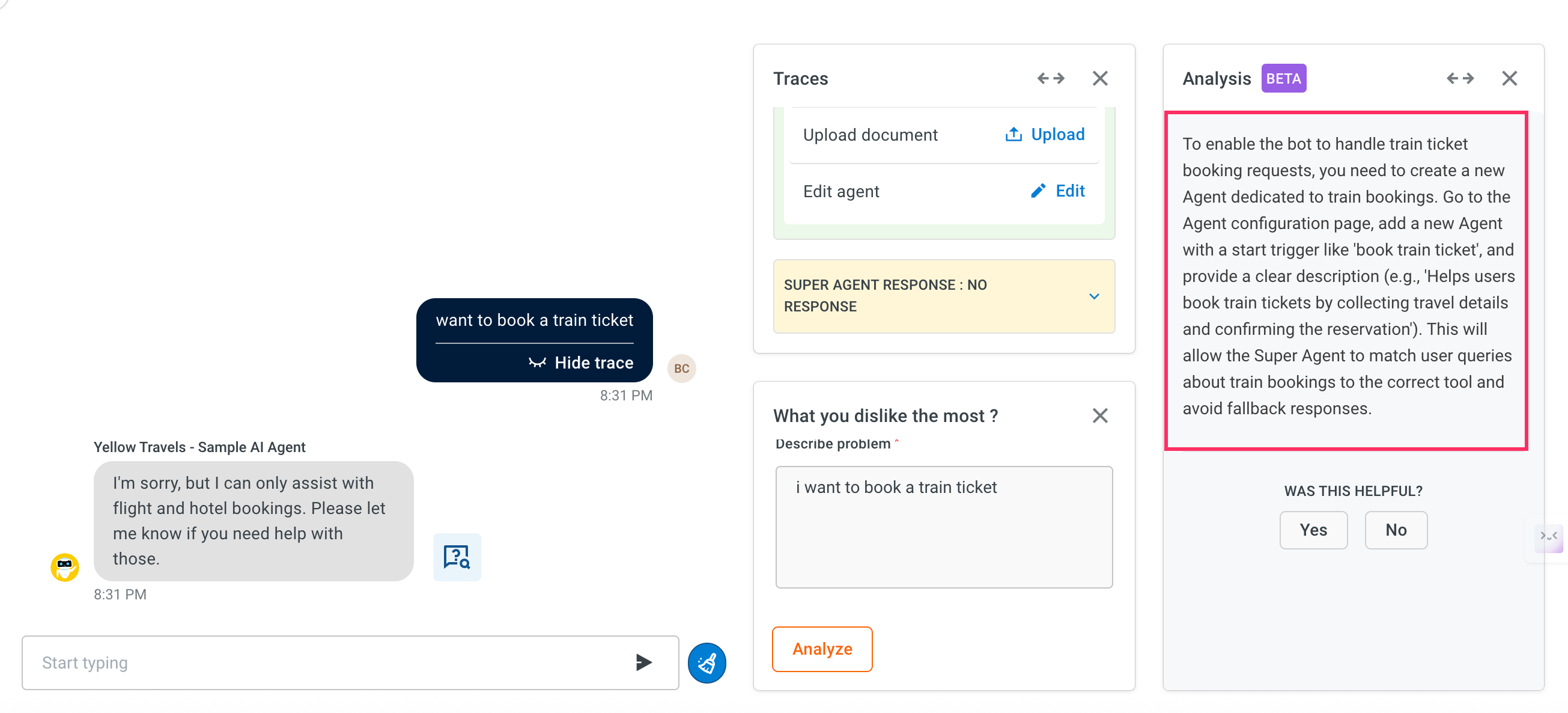
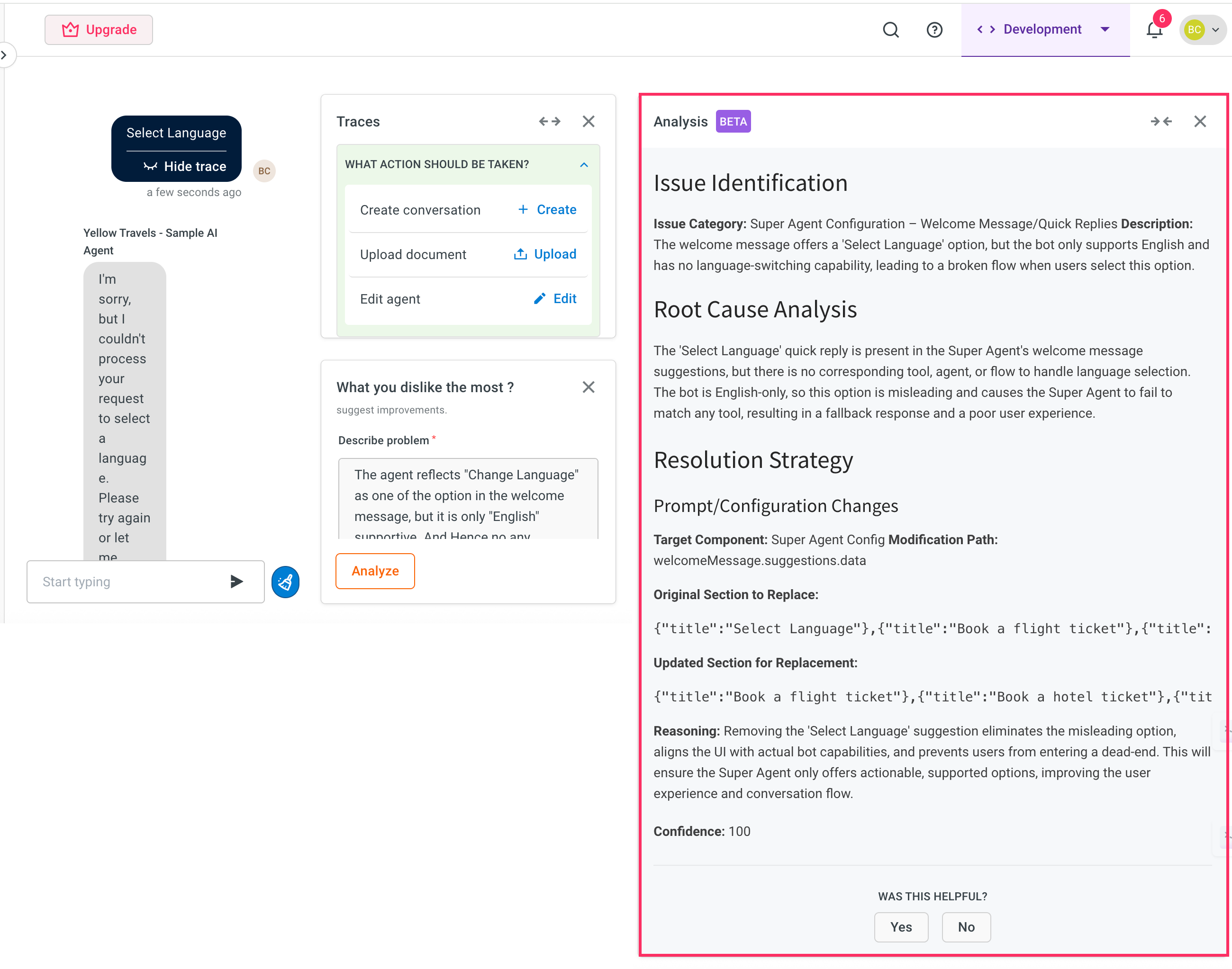
The debugger will process the input and displays a resolution strategy in the Analysis section. This helps you to understand what went wrong and how to fix it.
Outputs provided by the debugger
After analyzing your inputs and the existing agent setup, the debugger provides a structured output containing:
-
Issue identification: The debugger pinpoints the exact path in the agent configuration that caused the problem. This could be:
- A missing or misaligned prompt
- A broken workflow
- An incorrectly mapped API
- An unconfigured Knowledge base reference
This precise identification eliminates the need for manual trial and error and speeds up troubleshooting.
-
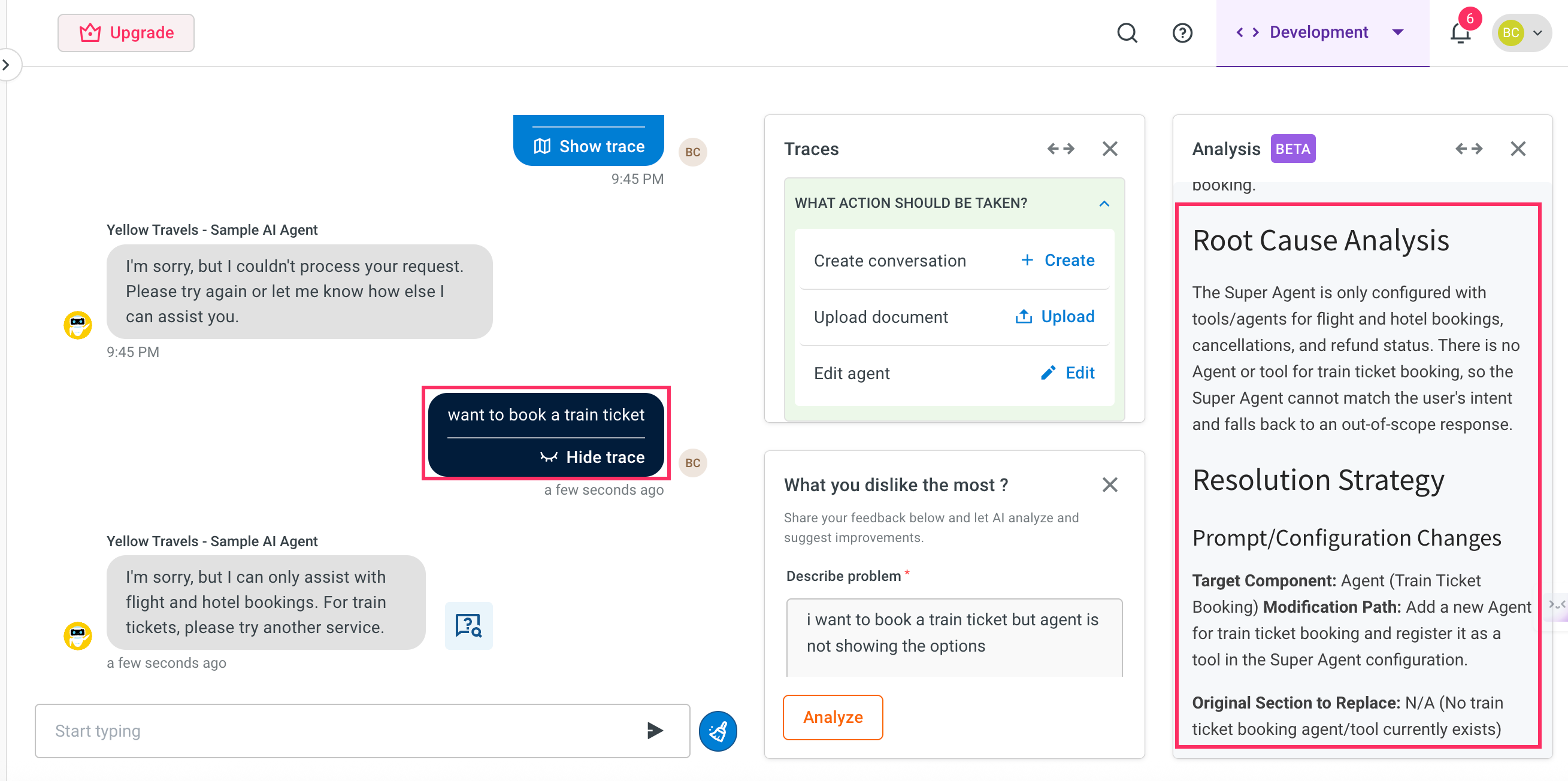
Root Cause Analysis(RCA): In certain cases, the debugger also provides a Root Cause Analysis. By understanding the root cause, you can improve your design and avoid repeating the same mistakes across agents or workflows. This is a brief explanation of what led to the issue, such as:
- Prompt was not mapped for this input
- Workflow lacks a step to fetch available flights
Example: If a flight booking confirmation fails, the debugger might identify that the workflow ends before a confirmation message is triggered, and explain that as the root cause.
-
Resolution strategy: A high-level explanation of what needs to change to fix the issue. This may include adding new logic, correcting a prompt, or updating a missing component.
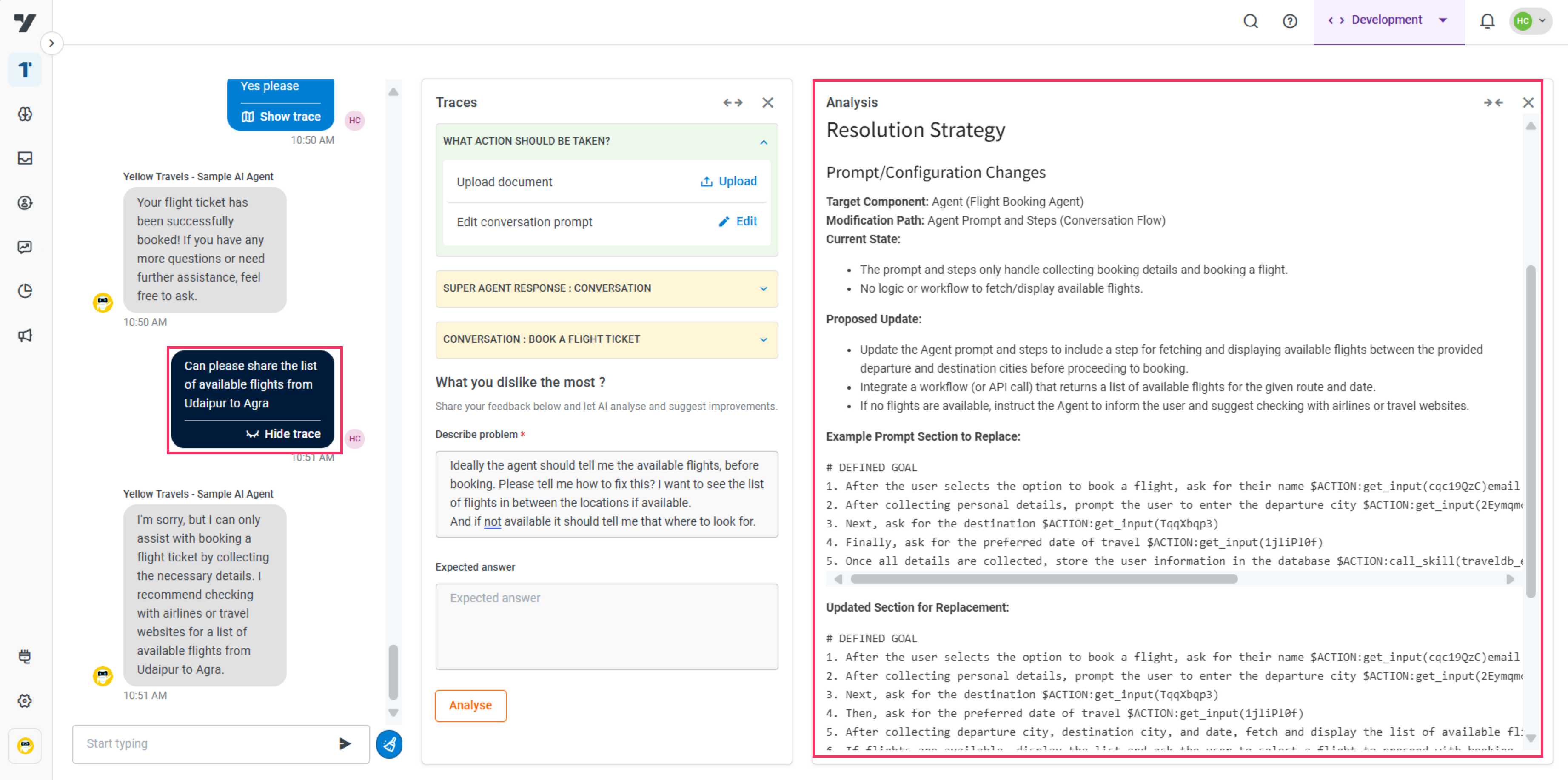
- Path: Shows exactly where the fix needs to be applied. For example, which agent, workflow, or prompt.
- Current: Displays the current state of the configuration in the identified section. This helps you understand what is missing.
- Updated section: Recommends a modified or complete version of the problematic section. This can often be copy-pasted or directly applied within the platform to resolve the issue.
-
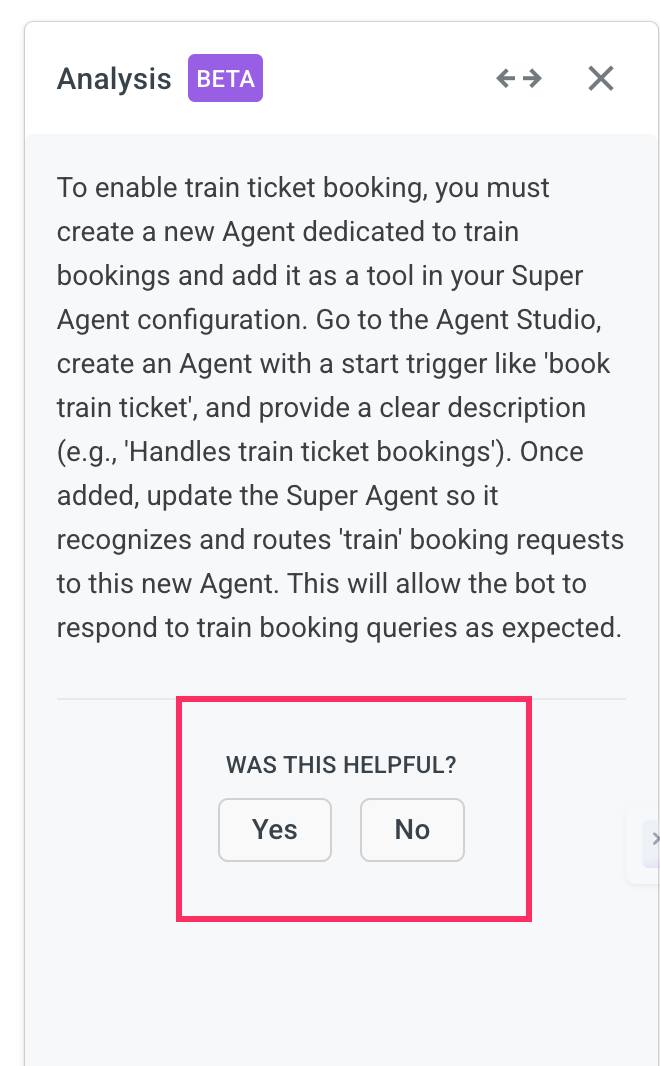
Was this helpful: Once the debugger provides the resolution strategy, you can rate the suggestion by selecting "Yes" or "No" under Was this helpful?. Your feedback helps improve the Copilot debugger’s accuracy and ensures better recommendations. Use this option to confirm whether the provided solution resolved your issue.
Sample Use cases
The Copilot debugger helps identify and resolve a wide range of issues across your AI agent setup. Below are common scenarios:
-
Prompt debugging: You describe that the AI agent is not responding correctly to "Book a train". The debugger checks and finds that there is no prompt configured for train bookings and suggests adding a missing prompt or routing logic.
-
Workflow fix: If the flight booking workflow fails to check flight availability before confirming, the debugger identifies the missing logic node in the flow. It recommends an updated version of the workflow that includes a step to validate available flights to ensure a complete booking experience.
-
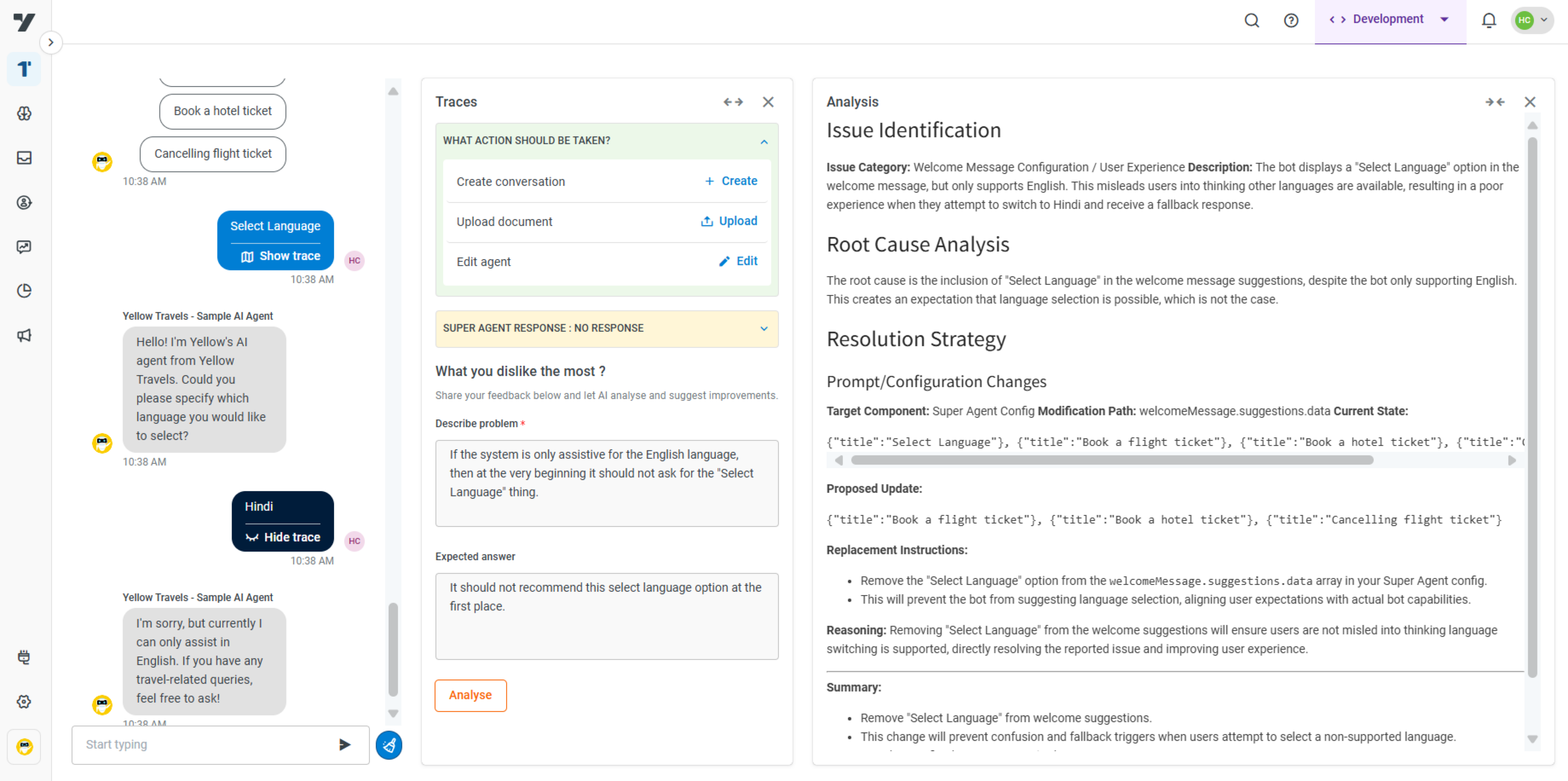
Super agent error: When the welcome message in the Super agent includes a "Change language" option, but the AI agent only supports English, users may be misled into expecting a language switch. The debugger detects this inconsistency and advises removing the "Change language" suggestion to better align with the AI agent's actual capabilities.
-
Knowledge base gap: If a user asks about refund policies and receives no response, the debugger checks whether the relevant knowledge base document exists, is indexed correctly, and is accessible to the agent. If it’s missing or misconfigured, it recommends uploading or properly tagging the document to ensure complete responses.