Configure data on default tables
You can configure data using the following options on the default tables:
- Push custom data: You have the capability to push custom data available in the user's 360 profile into the default tables.
- Secure data: You can enhance the security of your users' data, including personally identifiable information (PII) like names, email addresses, or phone numbers, by encrypting it.
Push custom data to default tables
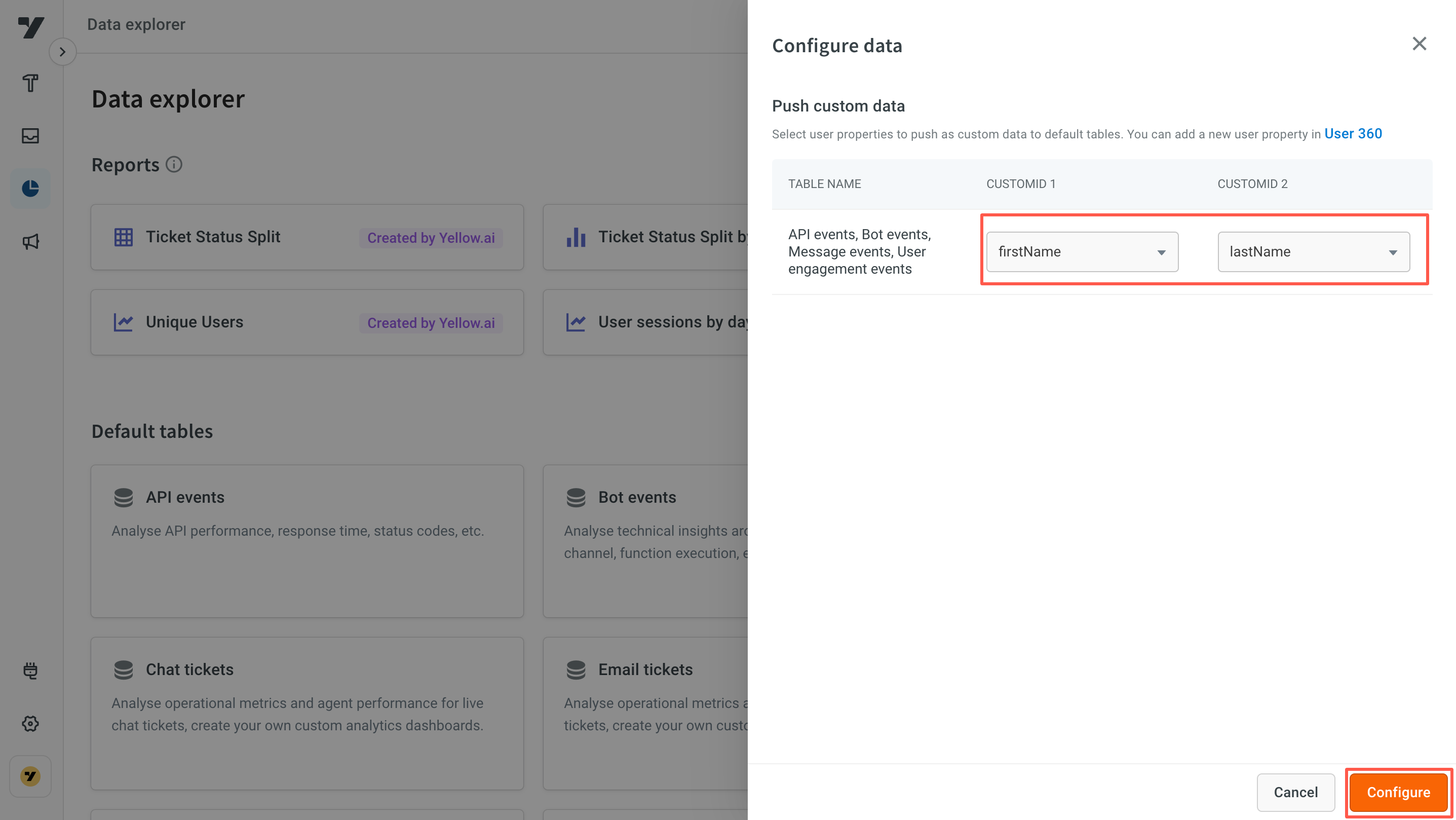
API events, Bot events, Message events, and User engagement events tables have two columns blank by default, CUSTOMID 1 and CUSTOMID 2. You can choose to push any of the user properties that are stored on user360 to all those default tables.
This action is irreversible. Once you configure it, the column(s) added will remain as a part of the default tables.
Steps to push custom data to default tables:
- Add a new user property on the user360 page.
- Click Data explorer > Configure.
- Select Map custom data. From the dropdown menu, choose a property (the custom data you want to push to API events, Bot events, Message events, and User engagement events tables) for CUSTOMID 1 and CUSTOMID 2.
- Click Configure and Add. Your custom data will get populated in the default tables.
CUSTOMID 2 can be added only after adding CUSTOMID 1.
Secure PII data on default tables
The Secure data feature allows users to encrypt personally identifiable information (PII) data during export and within the user interface of data explorer tables. This encryption of PII data applies to all users, with the exception of super admins, who will retain access to the unencrypted original data.
Follow the steps below to secure PII data within default tables:
- Click Data explorer > Configure.

- Enable the option to encrypt PII data and enter your Public key.
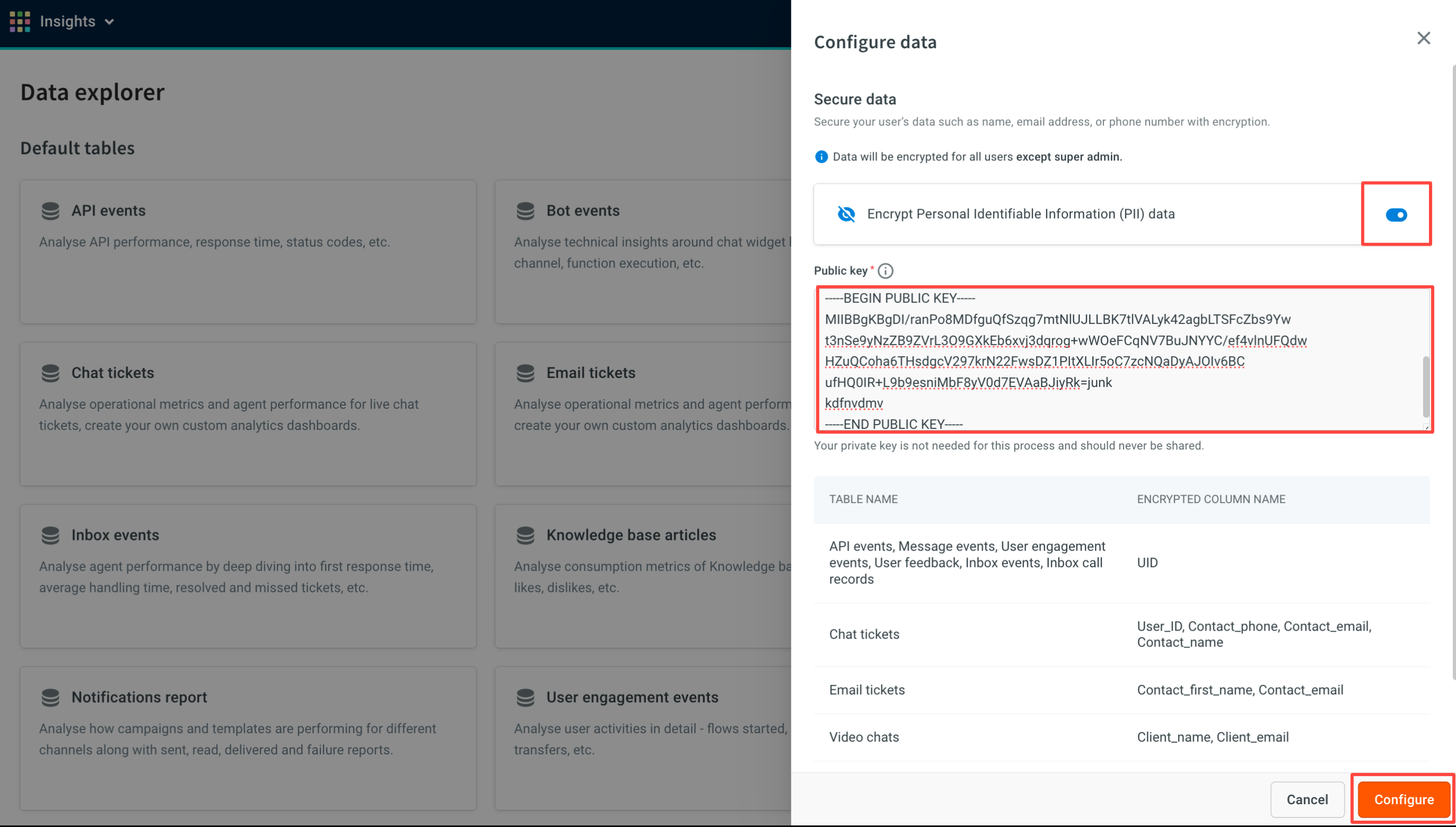
- A summary will be displayed, showing which tables and columns will be encrypted. This data will be encrypted in the table UI in Data Explorer, the table UI in Reporting, during export from Data Explorer, and during export from Data export.
Encrypted data:
| Tables | ColumnsColumns |
|---|---|
| API events | UID, BID |
| Message events | UID, BID |
| User engagement events | UID, BID |
| User feedback | UID |
| Inbox events | UID, AgentId |
| Inbox call records | UID |
| Chat tickets | User_ID, Contact_phone, Contact_email, Contact_name |
| Email tickets | Contact_first_name, Contact_email |
| Video chats | Client_name, Client_email |
| Notifications report | UserID, SenderID, cdpUserID |
| Call details report | SourceNumber, DestinationNumber |
| Leads | UID, BID |
| Conversations | UID, userName, replyTo, answeredBy |
| Bot tables | Masked columns will be encrypted (builder configuration) |
| Analytics (Under Custom Tables) | UID, BID |
- Click Configure to save the configuration and encrypt all PII data.
- Data will be encrypted for all users except Super Admin
- Configuration can be done by only Admins and Super Admin
- Aggregations on encrypted fields should be allowed
- Filters and groupBy on encrypted fields will not be possible
Steps to generate a public key
Follow these steps to generate the keys for encryption:
- Generate private key:
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096 -out private_key.pem
- Extract public key from private key:
openssl rsa -pubout -in private_key.pem -out public_key.pem
- Copy the public key and paste at Yellow Platform:
pbcopy < public_key.pem
The private key should be kept secure for decrypting encrypted data. Any tool that supports RSA decryption can be used with the key.
Sample code for decryption in Node.js
const crypto = require("crypto")
// Decrypt using the private key
const decryptRSA = (privateKey, encryptedData) => {
const encryptedDataBuffer = Buffer.from(encryptedData, 'base64');
const decryptedDataBuffer = crypto.privateDecrypt({
key: privateKey,
padding: crypto.constants.RSA_PKCS1_OAEP_PADDING,
oaepHash: "sha256"
}, encryptedDataBuffer);
return JSON.parse(decryptedDataBuffer.toString('utf-8'));
};
privateKey = `<YOUR PRIVATE KEY>`
encryptedData = "<cipherText>"
console.log(`decrytedData - ${decryptRSA(privateKey, encryptedData)}`);
Sample code for decryption in Python
from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization, hashes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
import base64
import json
# RSA private key in PEM format
private_key_pem = """<YOUR PRIVATE KEY>"""
cipherText = "<cipherText>"
# Load the private key
private_key = serialization.load_pem_private_key(
private_key_pem.encode(),
password=None,
backend=default_backend()
)
# Decode and decrypt the data
encrypted_data = base64.b64decode(cipherText)
decrypted_data = private_key.decrypt(
encrypted_data,
padding.OAEP(
mgf=padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256(),
label=None
)
)
print("Decrypted Data:", json.loads(decrypted_data.decode('utf-8')))
Sample code for decryption in Java
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.security.spec.MGF1ParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.PSource;
import javax.crypto.spec.OAEPParameterSpec;
public class RSADecryption {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String privateKeyPEM = "<YOUR PRIVATE KEY>"; // RSA private key in PEM format
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKeyFromString(privateKeyPEM);
// Base64-encoded encrypted data
String encryptedDataBase64 = "<cipherText>";
byte[] encryptedData = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedDataBase64);
// Decrypt the encrypted data using the private key
String decryptedText = decryptWithPrivateKey(encryptedData, privateKey);
System.out.println("Decrypted Text: " + decryptedText);
}
// Convert PEM private key string to PrivateKey object
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKeyFromString(String privateKeyPEM) throws Exception {
privateKeyPEM = privateKeyPEM
.replace("-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replace("-----END PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replaceAll("\\s+", ""); // Remove whitespace characters
byte[] privateKeyBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKeyPEM);
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
}
// Decrypt data using the private key
public static String decryptWithPrivateKey(byte[] encryptedData, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/OAEPWithSHA-256AndMGF1Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey, new OAEPParameterSpec("SHA-256", "MGF1", MGF1ParameterSpec.SHA256, PSource.PSpecified.DEFAULT));
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
return new String(decryptedBytes, "UTF-8");
}
}